nginx常用操作
开启
- 第一种方法 格式为: ngin地址 -c nginx配置文件位置
- 例如:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
停止
A:从容停止 需要知道进程号:
- 1,查看nginx进程号命令为:ps -ef|grep nginx 只需要查看master的进程号
- 2,停止命令 kill -QUIT 进程号
B:强制停止
- kill -9 进程号
配置文件校验
- 步骤一:进入sbin目录 命令 cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin 步骤二: ./nginx -t
- 或者 sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
重启
- 步骤一:进入sbin目录 命令 cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin 步骤二:./nginx -s reload
- 或者 sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
Nginx的web请求处理机制
Nginx结合多进程机制和异步机制对外提供服务,异步机制使用的是异步非阻塞方式。Nginx的master进程会生成多个worker进程,master进程负责管理这些worker进程的生命周期、接受外部命令、解析perl脚本等。而worker进程则用于接受和处理客户端请求。
每个worker进程能够使用异步非阻塞方式处理多个客户端请求。当某个worker进程接收到客户端的请求后,会调用IO进程处理,如果不能立即得到结果,worker进程就去处理其他的请求。当IO返回结果后,就会通知worker进程,而worker进程得到通知后,就会挂起当前正在处理的事务,拿IO返回结果去响应客户端请求,worker进程采用的是epoll事件驱动模型与IO进行通信的。epoll模型底层采用的是“回调callback”代替里轮询,使效率高于select模型。
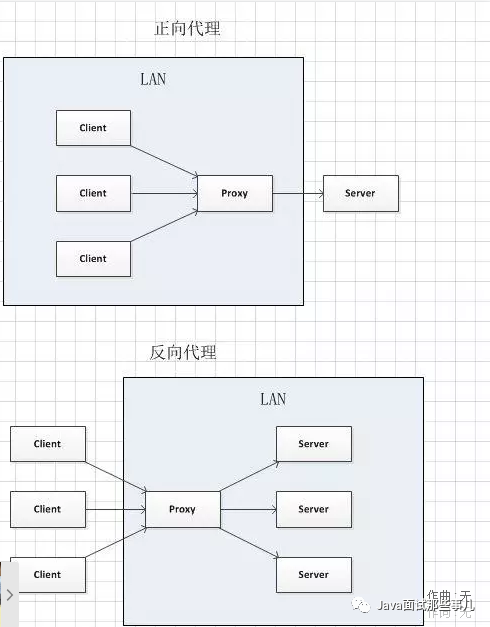
正向代理和反向代理
- 正向代理:
正向代理服务器是服务器的用户(客户端)架设的主机,与服务器无关,被访问的服务不知道用户真正的地址。 例如vpn访问 - 反向代理:
反向代理服务器和目标服务器对外就是一个服务器,暴露的是代理服务器地址,隐藏了真实服务器IP地址,用户不知道访问的服务真正的地址。 例如proxy_pass
server_name 和 upstream 和 proxy_pass
server_name
1. 介绍
server name 为虚拟服务器(单一主机或主机群上运行多个网站或服务的技术)的识别路径。因此不同的域名会通过请求头中的HOST字段(http1.1以上支持),匹配到特定的server块,转发到对应的应用服务器中去。
虚拟主机,就是将一台物理服务器虚拟为多个服务器来使用,从而实现在一台服务器上配置多个站点,即可以在一台物理主机上配置多个域名。Nginx中,一个server标签就是一台虚拟主机,配置多个server标签就虚拟出了多台主机。
2. 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25server {
listen 80;
server_name www.123.com;
location / {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua '
ngx.say("<p>first</p>")
';
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.zkh.com;
location / {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua '
ngx.say("<p>second</p>")
';
}
}
访问:www.123.com --> first
访问:www.zkh.com --> second
upstream
1. 介绍
常用负载均衡:能够将客户端的请求均匀地分发到后台各个应用服务器上,从而缓解服务器压力;并且当服务器出现宕机或者扩容时,也能正常运行。
2. 使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14http {
upstream web {
server 192.168.1.128:9200;
server 192.168.1.128:3000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location /
{
proxy_pass http://web;
}
}
}
proxy_pass
1. 介绍
反向代理:proxy_pass说明是动态请求,需要进行转发,比如代理到nodejs、java上
location 匹配规则
1. url匹配规则
1 | location [=|~|~*|^~|@] /uri/ { |
- =: 精确匹配后面的url
- ~: 正则匹配,区分大小写
- ~*:正则匹配,不区分大小写
- ^~:普通字符匹配, 如果该选项匹配,只匹配该选项, 一般用来匹配目录
- @: “@” 定义一个命名的 location,使用在内部定向时,例如 error_page
2. 匹配规则的优先顺序
- = 前缀的指令严格匹配这个查询。 如果找到则停止搜索
- 所有剩下的常规字符串,最长的匹配。 如果这个匹配使用^~前缀,搜索停止
- 正则表达式, 在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 如果第3条规则产生匹配的话,结果被使用。 否则,使用第2条规则的结果
3. alias 和 root 的区别
1. root: 实际访问文件路径会拼接URL中的路径
1 | location ^~ /tea/ { |
2. alias: 实际访问文件路径不会拼接URL中的路径
1 | location ^~ /tea/ { |
rewrite使用
rewrite 介绍
从功能看 rewrite 和 location 似乎有点像,都能实现跳转,主要区别在于 rewrite是在同一域名内更改获取资源的路径,而 location 是对一类路径做控制访问或反向代理,还可以proxy_pass(代理转发)到其他机器。
rewrite只能放在server{ },location{ },if{ }中,并且默认只能对域名后边的除去传递的参数外的字符串起作用
例如http://www.benet.com/abc/bbs/index.php?a=1&b=2 只对 /abc/bbs/index.php 重写
rewrite使用
1、语法
rewrite
flag不同参数:
last ∶本条规则匹配完成后,继续向下匹配新的location URL规则,一般用在 server和if中。
break ∶本条规则匹配完成即终止,不再匹配后面的任何规则,一般使用在 location 中。
redirect ∶返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址。
permanent ∶返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址。
2、案例
1 | location / { |