xhr、ajax、axios和fetch区别
xhr: 现代浏览器,最开始与服务器交换数据,都是通过XMLHttpRequest对象。它可以使用JSON、XML、HTML和text文本等格式发送和接收数据。
ajax: 为了方便操作dom并避免一些浏览器兼容问题,产生了jquery, 它里面的AJAX请求也兼容了不同的浏览器,可以直接使用.get、.pist。它就是对XMLHttpRequest对象的一层封装
Axios是一个基于promise的HTTP库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中。它本质也是对原生XMLHttpRequest的封装,只不过它是Promise的实现版本,符合最新的ES规范。
Fetch API提供了一个 JavaScript 接口,用于访问和操作HTTP管道的部分,例如请求和响应。它还提供了一个全局fetch()方法,该方法提供了一种简单,合理的方式来跨网络异步获取资源
axios的特性
基于Promise
支持浏览器和nodejs环境
可添加请求、响应拦截器和转换请求和响应数据
请求可以取消、中断
自动转换JSON数据
客户端支持方法XSRF
带着问题去看代码
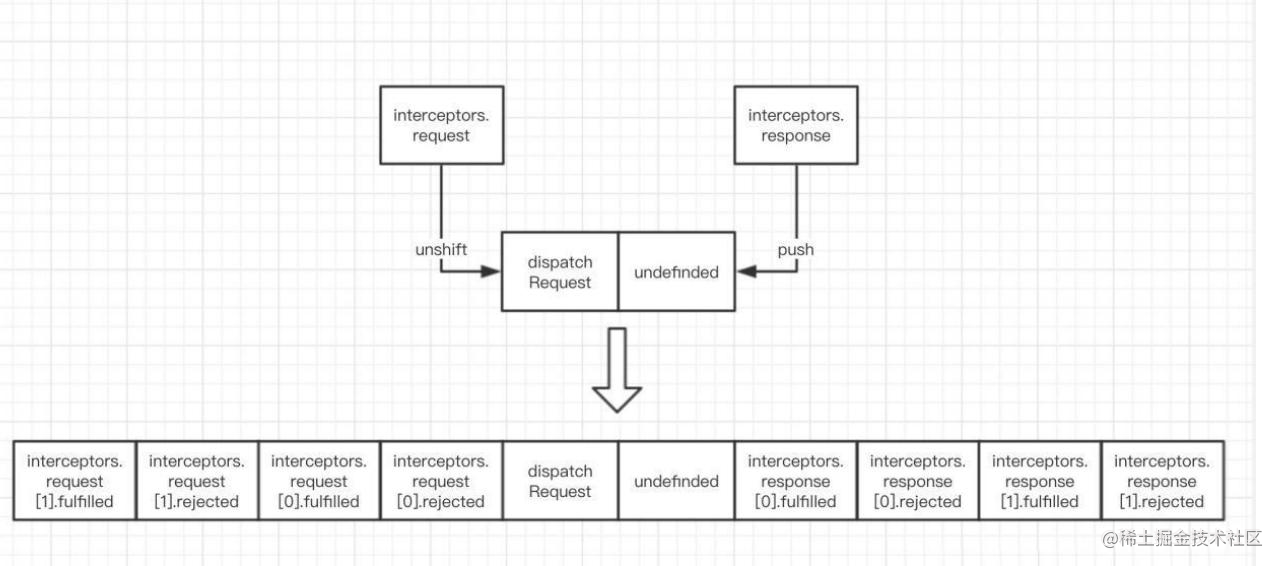
axios拦截器执行顺序?
源码分析 1、源码目录结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 ├── /lib/ └── /adapters/ ├── http.js ├── xhr.js └── /cancel/ └── /helpers/ └── /core/ ├──Axios.js ├── createError.js ├── dispatchRequest.js ├── InterceptorManager.js ├── mergeConfig.js ├── settle.js ├── transformData.js └── axios.js └── defaults.js └── utils.js
2、入口文件/lib/axios.js 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 function createInstance (defaultConfig ) const context = new Axios(defaultConfig); const instance = bind(Axios.prototype.request, context); utils.extend(instance, Axios.prototype, context, {allOwnKeys : true }); utils.extend(instance, context, null , {allOwnKeys : true }); instance.create = function create (instanceConfig ) return createInstance(mergeConfig(defaultConfig, instanceConfig)); }; return instance; } const axios = createInstance(defaults);axios.default = axios; export default axios
3. Axios.prototype.request 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class Axios constructor (instanceConfig) { this .defaults = instanceConfig; this .interceptors = { request: new InterceptorManager(), response: new InterceptorManager() }; } request(configOrUrl, config) { const requestInterceptorChain = []; let synchronousRequestInterceptors = true ; this .interceptors.request.forEach(function unshiftRequestInterceptors (interceptor ) if (typeof interceptor.runWhen === 'function' && interceptor.runWhen(config) === false ) { return ; } synchronousRequestInterceptors = synchronousRequestInterceptors && interceptor.synchronous; requestInterceptorChain.unshift(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); const responseInterceptorChain = []; this .interceptors.response.forEach(function pushResponseInterceptors (interceptor ) responseInterceptorChain.push(interceptor.fulfilled, interceptor.rejected); }); let promise; let i = 0 ; let len; if (!synchronousRequestInterceptors) { const chain = [dispatchRequest.bind(this ), undefined ]; chain.unshift.apply(chain, requestInterceptorChain); chain.push.apply(chain, responseInterceptorChain); len = chain.length; promise = Promise .resolve(config); while (i < len) { promise = promise.then(chain[i++], chain[i++]); } return promise; } len = requestInterceptorChain.length; let newConfig = config; i = 0 ; while (i < len) { const onFulfilled = requestInterceptorChain[i++]; const onRejected = requestInterceptorChain[i++]; try { newConfig = onFulfilled(newConfig); } catch (error) { onRejected.call(this , error); break ; } } try { promise = dispatchRequest.call(this , newConfig); } catch (error) { return Promise .reject(error); } i = 0 ; len = responseInterceptorChain.length; while (i < len) { promise = promise.then(responseInterceptorChain[i++], responseInterceptorChain[i++]); } return promise; } } export default Axios;
4. 拦截器实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class InterceptorManager constructor () { this .handlers = []; } use(fulfilled, rejected, options) { this .handlers.push({ fulfilled, rejected, synchronous: options ? options.synchronous : false , runWhen: options ? options.runWhen : null }); return this .handlers.length - 1 ; } eject(id) { if (this .handlers[id]) { this .handlers[id] = null ; } } clear() { if (this .handlers) { this .handlers = []; } } forEach(fn) { utils.forEach(this .handlers, function forEachHandler (h ) if (h !== null ) { fn(h); } }); } } export default InterceptorManager;
由于请求的发送需要在请求拦截器之后,在响应拦截器之前,所以数组先放入request,接着在数组的前后分别加入请求和响应拦截器,由于加入请求拦截器的方法是unshift,所以最后通过promise进行请求的链式调用的时候,我们可以看到执行顺序是从左往右的,所以最后注册的请求拦截器会最先执行,而响应拦截的执行顺序和注册顺序是一样的。
5、dispatchRequest 我们进入到核心请求方法dispatchRequest中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 function throwIfCancellationRequested (config ) if (config.cancelToken) { config.cancelToken.throwIfRequested(); } if (config.signal && config.signal.aborted) { throw new CanceledError(null , config); } } export default function dispatchRequest (config ) throwIfCancellationRequested(config); config.headers = AxiosHeaders.from(config.headers); config.data = transformData.call( config, config.transformRequest ); if (['post' , 'put' , 'patch' ].indexOf(config.method) !== -1 ) { config.headers.setContentType('application/x-www-form-urlencoded' , false ); } const adapter = adapters.getAdapter(config.adapter || defaults.adapter); return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution (response ) throwIfCancellationRequested(config); response.data = transformData.call( config, config.transformResponse, response ); response.headers = AxiosHeaders.from(response.headers); return response; }, function onAdapterRejection (reason ) if (!isCancel(reason)) { throwIfCancellationRequested(config); if (reason && reason.response) { reason.response.data = transformData.call( config, config.transformResponse, reason.response ); reason.response.headers = AxiosHeaders.from(reason.response.headers); } } return Promise .reject(reason); }); }
6、适配器adapter 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function getDefaultAdapter ( var adapter; if (typeof XMLHttpRequest !== 'undefined' ) { adapter = require ('./adapters/xhr' ); } else if (typeof process !== 'undefined' && Object .prototype.toString.call(process) === '[object process]' ) { adapter = require ('./adapters/http' ); } return adapter; }
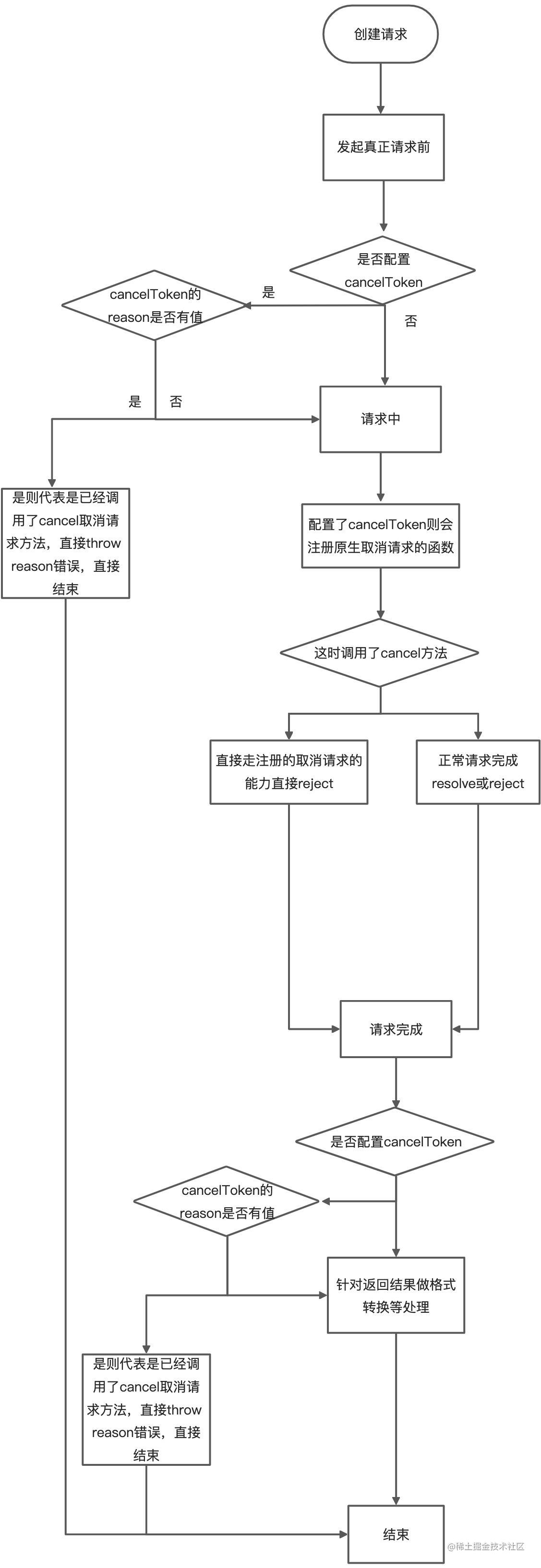
7、axios主动取消请求 终止一个尚未完成的网络请求, status状态为canceled
1、使用axios
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import { CancelToken } from axios;const source = CancelToken.source();axios .get('/user' , { cancelToken: source.token, }) .catch(function (thrown ) if (axios.isCancel(thrown)) { console .log('主动取消' , thrown.message); } else { console .error(thrown); } }); source.cancel('我主动取消请求' )
2、CancelToken构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 class CancelToken constructor (executor) { if (typeof executor !== 'function' ) { throw new TypeError ('executor must be a function.' ); } let resolvePromise; this .promise = new Promise (function promiseExecutor (resolve ) resolvePromise = resolve; }); const token = this ; this .promise.then(cancel => if (!token._listeners) return ; let i = token._listeners.length; while (i-- > 0 ) { token._listeners[i](cancel); } token._listeners = null ; }); this .promise.then = onfulfilled => let _resolve; const promise = new Promise (resolve => token.subscribe(resolve); _resolve = resolve; }).then(onfulfilled); promise.cancel = function reject ( token.unsubscribe(_resolve); }; return promise; }; executor(function cancel (message, config, request ) if (token.reason) { return ; } token.reason = new CanceledError(message, config, request); resolvePromise(token.reason); }); } throwIfRequested() { if (this .reason) { throw this .reason; } } subscribe(listener) { if (this .reason) { listener(this .reason); return ; } if (this ._listeners) { this ._listeners.push(listener); } else { this ._listeners = [listener]; } } unsubscribe(listener) { if (!this ._listeners) { return ; } const index = this ._listeners.indexOf(listener); if (index !== -1 ) { this ._listeners.splice(index, 1 ); } } static source() { let cancel; const token = new CancelToken(function executor (c ) cancel = c; }); return { token, cancel }; } } export default CancelToken;
3、请求中是如何处理的cancel1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 if (config.cancelToken || config.signal) { onCanceled = cancel => if (!request) { return ; } reject(!cancel || cancel.type ? new CanceledError(null , config, request) : cancel); request.abort(); request = null ; }; config.cancelToken && config.cancelToken.subscribe(onCanceled); if (config.signal) { config.signal.aborted ? onCanceled() : config.signal.addEventListener('abort' , onCanceled); } } let onCanceled;function done ( if (config.cancelToken) { config.cancelToken.unsubscribe(onCanceled); } if (config.signal) { config.signal.removeEventListener('abort' , onCanceled); } }
文章来源于
class static静态方法